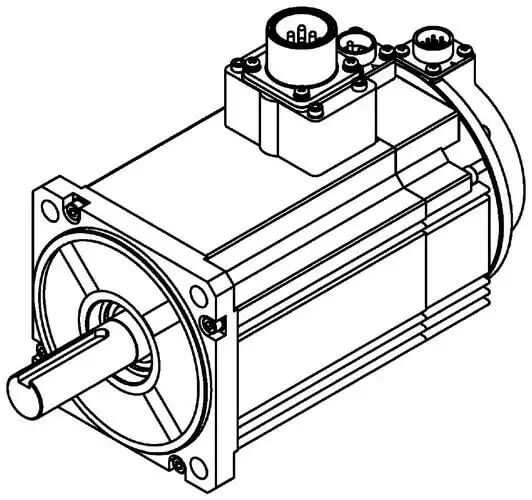
Servo Motor Shaft Essentials: Unlocking the Major Components of a Brushless Servo System
Why Read This Article?
Are you curious about how a servo motor works or which major components make it so versatile? If you manufacture automation equipment, integrate robotics systems, or design industrial and collaborative robots, then this guide is exactly for you. We, as a servo motor, Yaskawa Servo Motor, and Panasonic Servo Motor manufacturing plant for products, know first-hand the details that matter. In this post, we will uncover how the shaft, rotor, stator, and other components of a servo motor come together to deliver high-performance outcomes. Reading this will help you choose the right solutions, avoid damage to the motor, and drive better results in your automation or robotics projects.
1. What Is a Servo Motor and Why Does It Matter?
A servo motor is a special type of motor that uses a controller and sensor feedback to produce exceptional motion control. This servo motor is designed to manage speed and position, or even speed and direction, with a high degree of accuracy. It is often the core components in modern automation systems.
Key Points
- Servo motors are used in industrial servo solutions, robotics, and more.
- They typically include a servo driver or servo drive—an intermediary between the motor and the control system—which precisely manages the current to the motor.
- By reading feedback from an encoder, the servo motor adjusts to ensure the position of the motor matches the desired command, preventing damage to the motor.
Table: Basic Structure and Function
| Part | Role in Servo System |
|---|---|
| Controller | Sends commands to achieve desired motor output |
| Encoder | Feeds back the exact angle of the motor shaft |
| Servo Driver | Supplies regulated voltage and current |
| Shaft / Motor Shaft | The actual rotating end of the motor |
| Stator | Houses windings and provides electromagnetic field |
| Rotor | Rotates within the stator’s electromagnetic field |
This interplay between the encoder, the controller, and the motor’s mechanical design is what makes the servo system highly responsive and accurate in controlling servo motors.
2. How Does the Rotor and Stator Define Servo Motor Construction?
When we talk about servo motor construction, we must examine two main elements: the rotor and the stator. These main components serve as the mechanical heart of your servo motor. The motor typically has a brushless servo design (also known as a brushless dc or ac servo motor) for longevity and efficiency.
- Rotor
- The rotor in a brushless servo motor usually includes permanent magnets.
- It spins along the motor shaft, delivering mechanical energy to your machinery or robot.
- Rotor inertia influences how quickly the servo motor can accelerate or decelerate.
- Stator
- The stator remains stationary, with winding arrays that create changing electromagnetic fields.
- In a synchronous motor version (like many modern industrial servo motors), the stator’s rotating fields match the rotor’s rotation.
- Stator design impacts motor power, heat dissipation, and overall motor specifications.
Quote: “A servo motor consists of both a rotor and a stator, combining for precise motion control even at varied loads.”
Case Study
Imagine an industrial servo application in a collaborative robot. Thanks to advanced stator designs, you can sustain stable torque even when the manipulator’s shaft is loaded near maximum capacity. Meanwhile, the rotor inertia remains low enough to allow swift changes in speed and direction.
3. What Are the Advantages of Servo for Industrial Applications?
The advantages of servo solutions are manifold. We at our servo motor manufacturing plant—specializing in Yaskawa Servo Motor and Panasonic Servo Motor lines—often see how these benefits empower businesses, including industrial robots and collaborative robots manufacturers, and automation equipment manufacturers.
Key Advantages
- Precise Motion Control: With an integrated encoder, you get real-time feedback. This leads to pinpoint accuracy in rotational or translational motor tasks.
- High Efficiency: Servo motors are more complex than standard induction motors or stepper motors, but they deliver energy savings and stable operation.
- Versatility: They’re used in applications requiring quick acceleration, deceleration, and smooth control.
- Motor capable of consistent torque: This ensures reliability under demanding loads.
Bullet List
- Servo motors provide immediate response to changing loads.
- Motors are ideal for pick-and-place tasks, packaging lines, and robotic arms.
- They are well-suited for motion control where feedback from a sensor is essential.
- Servo motors are widely used in electronics assembly, automotive manufacturing, and more.
Chart: Comparing Standard vs. Servo
| Feature | Standard DC Motor (dc motor) | Servo Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Control Precision | Limited | Highly accurate |
| Torque Consistency | Medium | Very stable under load |
| Controller Complexity | Lower | Higher, but flexible |
| Heat Management | Basic | Advanced design |
| End Use | Simple tasks | Used in applications requiring fine control |
4. How Do I Control the Servo Motor for Precise Motion Control?
Controlling servo motors involves a control system that reads sensor data and issues commands. The servo controller or control circuit manipulates the voltage input to your servo, typically using pulse width modulation (PWM). This modulation determines the angle of the motor shaft and can also set the speed and position.
- Feedback Loop
- The encoder or other feedback components measure the position of the motor.
- The servo system compares actual position with the desired one.
- Any discrepancy triggers an adjustment in current to the motor to correct the difference.
- Command Signals
- Many servo motors support a standard PWM signal if it’s a standard servo or an rc servo.
- For brushless servo systems like Yaskawa Servo Motor products, a more sophisticated servo drive is used for advanced dynamic control.
- Avoiding Damage
- Always check the servo datasheet to prevent motor failure from overvoltage or exceeding torque limits.
- If the size of the servo is too small for your load, you risk damage to the motor when loads exceed capacity.
Chart: Simplified Control of the Servo Motor
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1. Input Command | Desired angle or velocity is sent to the controller |
| 2. PWM Signal Output | Servo controller sets the pulse width modulation |
| 3. Feedback Reading | The encoder checks actual motor shaft position |
| 4. Adjustment | The system corrects errors by boosting or reducing voltage |
5. Which Type of Servo Motor Is Right for You?
Choosing the type of servo motor can be overwhelming, as there are several types: dc servo motor, ac servo motor, brushless servo motor, and more. You might also weigh series servo vs. a single unit servo. But how do you pick the right servo motor?
Different Types of Servo Motors
- AC Servo Motor / Synchronous AC Servo Motor: Favored in heavy-duty tasks. Often rely on permanent magnet motors.
- Brushless Servo Motor: High efficiency, low maintenance, minimal heat generation.
- DC Servo Motor: Simpler electronics, but less robust for complex industrial tasks.
Insight: Servo motors are often chosen over induction motors for high-precision tasks. Meanwhile, stepper motors could be an alternative for simpler positioning but lack dynamic feedback.
Factors to Consider
- Motor Specifications: Evaluate your torque, speed, and power needs. If you want motors with high power, that might lead you to a brushless servo design.
- Motor Operates Environment: High humidity, temperature extremes, etc.
- Servo motor’s feedback: The encoder type can be incremental or absolute.
- Applications: Industrial servo or series servo motor might handle large loads, whereas a smaller continuous rotation servo suits simpler tasks.
Data: We found that many servo-based systems can yield up to 25% improvement in throughput compared to older, purely mechanical solutions.
6. How Are AKMA Servo Motors Revolutionizing the Industry?
AKMA servo motors are a trending name in high-performance motion control circles. This series servo approach focuses on:
- Core Components: From the robust stator build to advanced rotor materials, AKMA servo motors are engineered for durability.
- Control of the Servo Motor: Their integrated electronics make controlling servo motors simpler while delivering stable torque.
- Intermediary Between the Motor & System: By upgrading the servo drive, you can reduce downtime and significantly boost reliability.
Case Study
A user deploying akma servo motors in industrial servo lines reported a 30% reduction in production cycle times. The controller easily adapted to new tasks with minimal setup, saving engineering hours.
Pro Tip: If you’re working with automation equipment manufacturers and system integrators, or are in the field of industrial robots and collaborative robots, consider specialized AKMA units for the next level of integration.
7. FAQ on Controlling and Checking the Servo Motor
- How do I set up a servo drive for a brushless servo motor?
You typically connect your servo drive to the servo motor via dedicated cables for power and feedback. The servo controller or control system sets your motion profile. Always ensure correct voltage and pinouts to avoid issues. - What if the servo can move but loses steps under load?
If your servo is skipping or stalling, it may mean the motor is undersized for the torque needed. Damage to the motor can occur if you keep pushing it. Check the servo capacity or upgrade to a bigger unit with a stronger motor shaft and a more powerful controller. - Does a servo motor must be brushless to be industrial-grade?
Not necessarily. Some users pick brushed or dc servo motor setups for smaller tasks. Still, a brushless servo or ac servo motor is standard for heavy industrial lines because it offers less maintenance and better efficiency. - Why do servo motors provide precise motion?
Their integral feedback components—like an encoder—plus a dedicated control circuit let the servo system micro-adjust speed and position or speed and direction in real time. This synergy of electronics and mechanics is why servo motors are more complex but extremely reliable motors. - What if I see motor failure messages on the servo driver?
This can result from overheated windings, excessive load, or wiring faults. Checking the controller logs or specifications of the motor helps. Also, confirm that your voltage supply meets the servo motor requirements.
Random Image #1
Random Image #2
Where to Learn More or Buy
If you want to see real examples of top-tier servo products, check out:
- SGD7S-3R8A10A Original Yaskawa Single axis servo driver
- SGD7S-470A00A Original Yaskawa Single axis servo driver
- Visit Servo Motor Store main page for more solutions
- Panasonic Servo Motor Selections
- High-Power Yaskawa Single Axis Servo Driver Options
These links showcase real solutions for advanced servo system integration.
Bullet Point Summary: Most Important Things to Remember
- Servo motor basics: A servo motor combines a rotor, stator, and feedback (e.g., encoder) to deliver precise motion.
- Major components: Look to the shaft, stator, rotor, and electronics as the part of a servo motor that fosters synergy in motion control.
- Brushless servo motor or ac servo motor designs often yield the best durability and performance.
- Torque capacity: Always confirm the load and speed demands so you avoid damage to the motor.
- Controlling servo motors requires a dedicated controller or servo controller plus the correct servo drive.
- If your tasks call for precise motion control, always ensure your servo motor has enough capacity, voltage headroom, and robust feedback components.
- Advantages of servo revolve around energy efficiency, accuracy, and quick dynamic response—perfect for industrial servo lines, especially in automation equipment or collaborative robots.
- From akma servo motors to dc servo motor variations, you can tailor solutions for the best fit.
- Double-check motor specifications to prevent oversizing or undersizing.
- We, as servo motor, Yaskawa Servo Motor, and Panasonic Servo Motor manufacturers, are here to guide you, from selecting the right servo motor to optimizing performance.
Ready to talk details? Our team at the manufacturing plant stands by to help you find reliable motors with several types and motors provide precise motion. If you’re an automation equipment manufacturer, system integrator, or involved in building industrial or collaborative robots, connect with us to discover how our servo motors elevate your next big project.